Which of the Following Allows Faster Conduction of Nerve Impulses
Five-year-old Amy wakes her parents up at 3 AM crying and complaining of a sore neck a severe headache and feeling sick to her stomach. It is made up of protein and fatty substances.
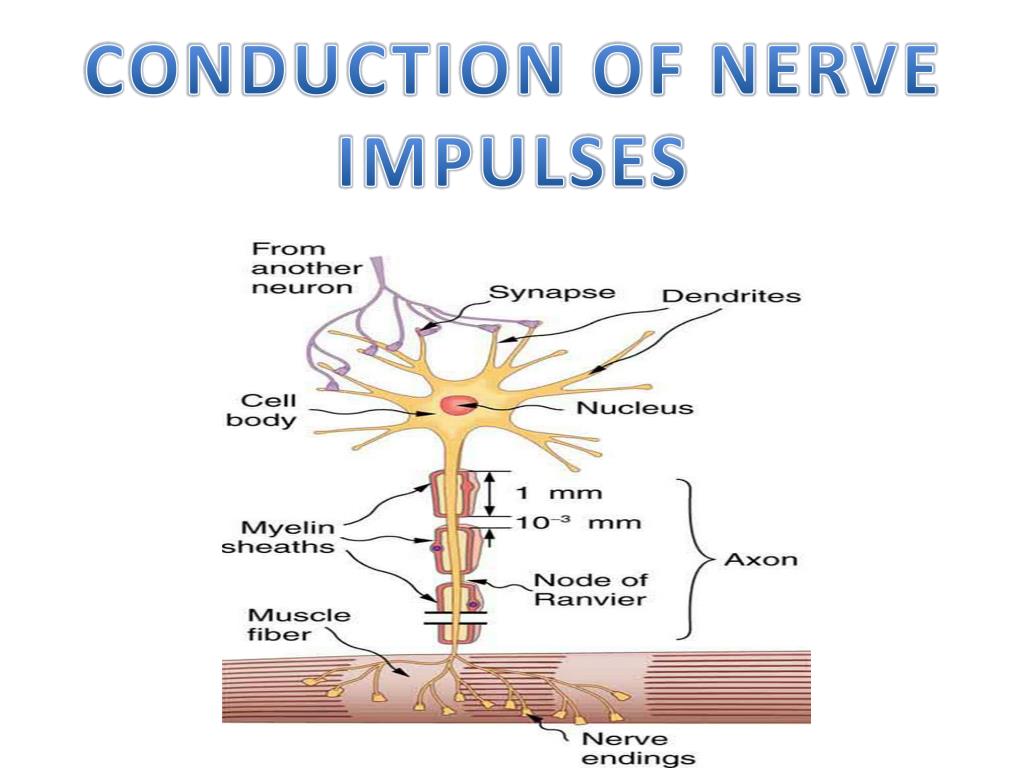
Ppt Conduction Of Nerve Impulses Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4206308
Myelinated axons conduct impulses about 10 times faster than comparable unmyelinated ones.

. The messages cant get sent. о A small fiber with multiple Schwann cells A small unmyelinated fiber O A large unmyelinated fiber 0 o A small diameter myelinated fiber A large diameter myelinated fiber O QUESTION 3 Match the anatomical term regarding the neuron to. Which of the following is a role of CSF.
Explain why increasing the axon diameter also increases the speed of impulse conduction. C increased magnitude of the potential difference during an action potential. What is the speed of conduction up to in a Group A axon.
She has a temperature of 40 circ mathrm C left 104 circ mathrm Fright and hides her eyes saying that the lights are too bright. A faster conduction of nerve impulses. D saltatory conduction of action potentials.
Axon diameter- More diameter of axon accounts for more generation and conduction of nerve impulses. Where is the speed of nerve impulses faster. O E All of these are correct.
In fast fibres eg. The nerve impulse travels at a speed of 100 ms in saltatory conduction. 0 D Continuous conduction is slower than saltatory conduction.
Explain why MS impairs nervous system function even though the axons are still intact. Myelin is composed of lipids and proteins primarily myelin basic protein MBP and oligodendrocytes. Saltatory conduction is faster because the action potential basically jumps from one node to the next saltare to leap and the new influx of Na renews the depolarized membrane.
All of the following are associated with the myelin sheath EXCEPT. The presence of a myelin sheath increases the speed of conduction of nerve impulses. C Saltatory conduction requires more ATP than continuous conduction.
It increases with increase in diameter of the nerve fiber iii. Myelin is an insulating layer or sheath that forms around nerves including those in the brain and spinal cord. In a slow nerve fibre with a conduction velocity of 2 metres per second an action potential with a duration of 2 milliseconds would occupy about 4 mm of nerve.
So marine invertebrates which live at temperatures nearby 0C have developed thick nerves to speed up their responses. Myelin is a lipid bilayer that forms the insulation around axons to help speed up nerve impulse conduction. 150 ms or 300 mph.
Increase surface area of cerebral cortex provide protection provide buoyancy allow for faster conduction of nerve impulses. X 6 Which of the following is true of nerve impulse conduction A Saltatory conduction occurs on unmyelinated axons. Myelin speeds the conduction of nerve impulses by a factor of 10 compared to unmyelinated fibers of the same diameter.
Conduction occurs in myelinated axons. Nerve Diameter - The larger the diameter the faster the speed. Automatic Nervous system sensory and.
The sheath insulates the axon and covers up the section beneath it. The following statements are true about signal conduction along myelinated fibers. Transcribed image text.
Saltatory conduction means that the impulse is regulated by the axons and dendrites working in unison. It is 50-100 times faster in myelinated fiber compared to unmyelinated ii. Which of the following allows faster conduction of nerve impulses.
Nervous system and endocrine systems. O B Continuous conduction occurs on myelinated axons. Myelin speeds the conduction of nerve impulses by a factor of 10 compared to unmyelinated fibers of the same diameter.
Myelinated nerve fibres- Generation and conduction of nerve impulses get faster in the myelinated nerve fibres than unmyelinated nerve fibres. Saltatory conduction means that the impulse starts at the cells nucleus rather than at the axon hillock. This myelin sheath allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along the nerve cells.
Nerve signals transmit much faster than in continuous conduction because an action potential is generated only at the neurofibrils segments of axon without myelination of myelinated axon rather than along the entire length of unmyelinated axon. B nodes of Ranvier forming gaps along the axon. Describe the adaptive advantage of faster conduction of nerve impulses.
Neurons - Nerve Impulses A living organism is made up of different types of cells which help them to control and coordinate with their surroundings. In an animal body coordination is the effective outcome of two systems ie. Temperature - The faster the speed the higher the temperature.
If myelin is damaged these impulses slow down. Squid giant axon the conduction velocity is up to 70 ms and a 1msec action potential would occupy about 70mm of the axons length. Nerve impulse propagates by jumping from one node of Ranvier to the next.
The velocity of conduction of the action potential along the nerve fiber depends on following factors. Along with the myelination of the axon the diameter of the axon can influence the speed of conduction. This makes the process of nerve impulse faster as the nerve impulse does not travel the entire length of the axon this happens in case of continuous conduction.
Saltatory conduction means that the nerve impulse seems to jump from one node to the nextand is regenerated as it speeds along. The emergency physician suspects meningitis. What is the propagation speed of an action potential moving by continuous propagation.
What increases speed of nerve impulse conduction. Which of the following allows faster conduction of nerve impulses. Where is the speed of nerve impulses slower.
Increase in temperature increases velocity iv. Where can you find Group B axons. QUESTION 2 Conduction of a nerve impulse would be the fastest in which of the following.
Factors affecting generation and conduction of nerve impulses are-a. This is the reason behind squids having very large size nerves. Which of the following allows faster conduction of nerve impulses.
Reduces resistance of the message. So homoeothermic warm-blooded animals have very faster.
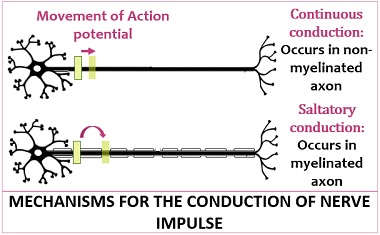
What Is Nerve Impulse Definition Conduction Transmission Functions Biology Reader


No comments for "Which of the Following Allows Faster Conduction of Nerve Impulses"
Post a Comment